Sustainable Solutions: Green Cloud Computing Architecture
Summary
Green cloud computing is an evolving approach that integrates sustainability into cloud infrastructure, aiming to reduce environmental impact while maintaining performance and cost-efficiency. As data centers account for a significant share of global energy consumption, this shift is both a necessity and an opportunity.
Table of Contents
Green Cloud Computing
Definition and Importance
Cloud Computing: On-demand IT resources (servers, storage, databases) over the internet, scalability, and cost efficiency.
Green Cloud Computing: Sustainability integrated into cloud infrastructure, energy efficiency, renewable energy, and reduced carbon footprint.
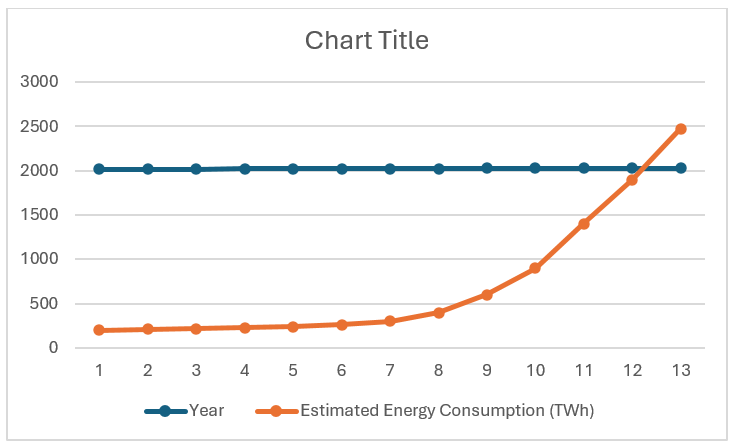
Why Sustainability: Data centers consume ~2% of global electricity, 3.21% in the EU by 2030 and . Green cloud computing optimizes energy use and reduces environmental harm.
Historical Context
Evolution of Cloud: From mainframes to virtualized, distributed systems, the cloud has evolved to meet demand.
Green Initiatives: Rising energy costs and environmental awareness drove tech giants like AWS, Google, and Microsoft to go renewable and efficient.
Environmental Concerns: Regulations (e.g. carbon taxes) and consumer demand for ethical practices accelerated green IT adoption.
Current Trends and Stats
- Market Size: Green data center market reached $35.58B in 2021, 7.6% CAGR.
- Energy Usage: Data centers use 1.3% of global electricity, the same as the airline industry.
- Adoption: 90% of AWS is on renewable energy, and Google aims to be 100% carbon-free by 203
Green Cloud Computing Principles
Environmental Sustainability
- Resource Efficiency: Virtualization consolidates servers, 3-5x less physical hardware.
- Renewable Energy: Solar, wind, and hydropower data centers, AWS, and Azure aiming for 100% renewable by 2025.
- Waste Management: Recycling e-waste and low-carbon materials in hardware.
Economic Viability
- Cost Savings: Energy efficient cooling (e.g. liquid immersion) 20-30% operational cost savings.
- Financial Incentives: Tax breaks for LEED-certified buildings and Energy Star compliance.
Social Responsibility
- CSR: Companies like Salesforce have net zero emissions, which also enhances brand reputation. Consumer Demand: 60% of consumers prefer eco-friendly brands, driving cloud providers to go green.
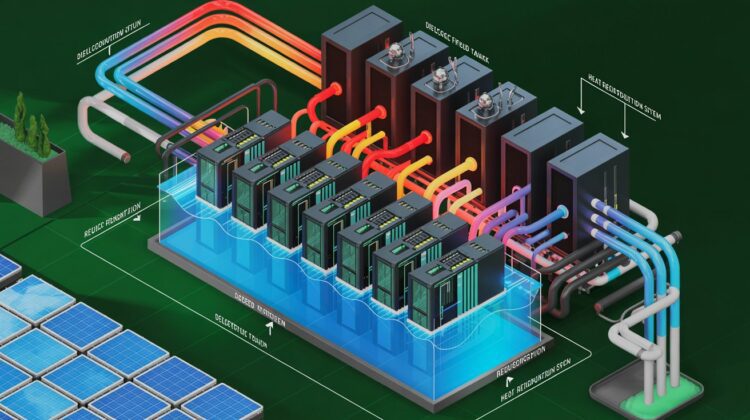
Green Cloud Architecture Components
Energy Efficient Data Centers
- Design: Modular layout, hot/cold aisle containment, and geothermal cooling.
- Cooling Innovations: Liquid immersion cooling consumes 40% less energy than air cooling.
- Virtualization: Reduces server count, energy, and space requirements.
Cloud Service Models
- IaaS/PaaS/SaaS: SaaS has the lowest carbon footprint as it has shared resources.
- Multi-Cloud Strategies: Distribute workloads to regions with renewable energy, and minimize latency and emissions.
Optimized Resource Management
- Load Balancing: AI-driven auto-scaling eliminates idle servers 215.
- Monitoring Tools: Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) metrics track efficiency (ideal PUE = 1).
Challenges and Obstacles
Technological Limitations
- Legacy Systems: Retrofitting old data centers with green tech is expensive.
- Scalability: High-density computing (e.g. AI) strains cooling systems.
Economic Constraints
- High Initial Costs: Building green data centers requires 20-30% more upfront investment.
Regulatory Issues
- Compliance: Meeting LEED or Energy Star standards involves rigorous audits.

Future Directions and Innovations
Emerging Technologies
- AI/ML: Predict energy usage and optimize workloads.
- Nuclear Power: Small modular reactors (SMRs) for low carbon energy for data centers.
Policy Evolution
- Global Standards: The Green Grid’s PUE and CUE metrics drive industry-wide adoption.
Collaborations
- Partnerships: IBM and Microsoft partner with NGOs for reforestation and water conservation
FAQ
Q1. What is the green cloud?
A: An eco-friendly approach to cloud infrastructure that uses less energy and less carbon.
Q2. How do data centers measure energy efficiency?
A: Using Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) where lower ratios are better.
Q3. What are the benefits of green cloud architecture?
A: Lower costs, compliance, and better brand reputation



